Transthoracic Echocardiogram
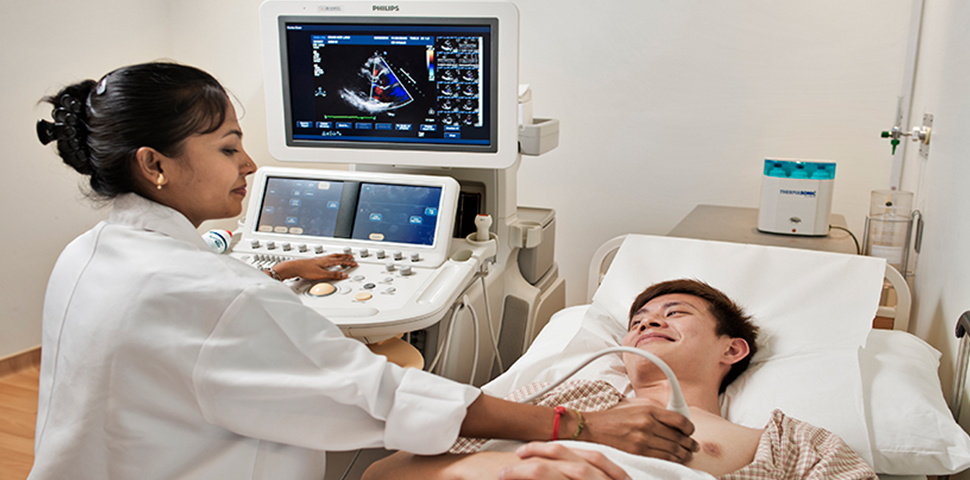
An echocardiogram shows the anatomy, structure and function of your heart.
Echocardiography is a type of ultrasound test which is used to measure the structure and function of the heart walls and valves. During the test, sound waves are emitted through your skin using a handheld device called a transducer. These waves bounce off your heart and return signals to a computer, which uses those signals to create images that show the heart and the blood flow through your heart and the vessels around it. Echocardiography plays an important role in the diagnosis and management of many different types of heart disease.
Echocardiography is used in the diagnosis, management and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic tests in cardiology. It can provide information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, and the location and extent of any tissue damage. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes).
Echocardiography is non-invasive and it usually takes 20-30 minutes.

