My Heart Scan
A Heart Ultrasound Scan(also called Echocardiogram) shows the anatomy, structure and function of your heart.
The Heart Scanning facility at My Heart Clinic is a state-of-the-art centre with a tradition of clinical excellence, education and innovation.
At My Heart Clinic we provide the most efficient and professional heart ultrasound scanning service
Our heart scan specialists have the experience and expertise to provide treatment options with the latest equipment.
What is an Ultrasound Heart Scan (Echocardiogram)?
Echocardiography is a type of ultrasound test which is used to measure the structure and function of the heart walls and valves. During the test, sound waves are emitted through your skin using a handheld device called a transducer. These waves bounce off your heart and return signals to a computer, which uses those signals to create images that show the heart and the blood flow through your heart and the vessels around it. Echocardiography plays an important role in the diagnosis and management of many different types of heart disease.
Echocardiography is used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic tests in cardiology.
Why Echocardiogram is performed?
Heart Ultrasound Scan can provide information about :
- Overall function of your heart such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes).
- Thesize and shapeof the heart (internal chamber size quantification)
- Pumping capacity, and the location and extent of any tissue damage.
- Determine the presence of many types of heart disease, such as valve disease, myocardial disease, pericardial disease, infective endocarditis, cardiac masses and congenital heart disease.
- Follow the progress of valve disease over time.
- valuate the effectiveness of your medical or surgical treatments.
Echocardiography is a non-invasive and it usually takes 20-30 minutes.
Staff at My Heart Clinic has unique expertise and experience in performing heart scan (echocardiography) studies.
The Echocardiography facility offers imaging tests including 2-D and 3-D echocardiography, as well as complex Doppler studies that doctors may use to check the blood flow and pressures inside the heart.
The Echocardiography facility also offers evaluation of vascular health in blood vessel studies, allowing staff to detect early changes related to atherosclerosis. The Ultrasound Scan also offers carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) testing and tests of other indications of vascular function, including aortic pulse wave velocity and brachial artery reactivity. These tests, along with a clinical evaluation, help doctors tailor each person's medical care and lifestyle counselling.
Transthoracic echocardiogram
In this standard type of echocardiogram:
- A technician (sonographer) spreads gel on a device (transducer).
- The sonographer presses the transducer firmly against your skin, aiming an ultrasound beam through your chest to your heart.
- The transducer records the sound wave echoes from your heart.
- A computer converts the echoes into moving images on a monitor.
If your lungs or ribs block the view, you may need a small amount of an enhancing agent injected through an intravenous (IV) line. The enhancing agent, which is generally safe and well tolerated, will make your heart's structures show up more clearly on a monitor.
Transoesophageal echocardiogram
If your doctor wants more-detailed images or it's difficult to get a clear picture of your heart with a standard echocardiogram, your doctor may recommend a transoesophageal echocardiogram.
In this procedure:
- Your throat will be numbed, and you'll be given medications to help you relax.
- A flexible tube containing a transducer is guided down your throat and into the tube connecting your mouth to your stomach (esophagus).
- The transducer records the sound wave echoes from your heart.
- A computer converts the echoes into detailed moving images of your heart, which your doctor can view on a monitor.
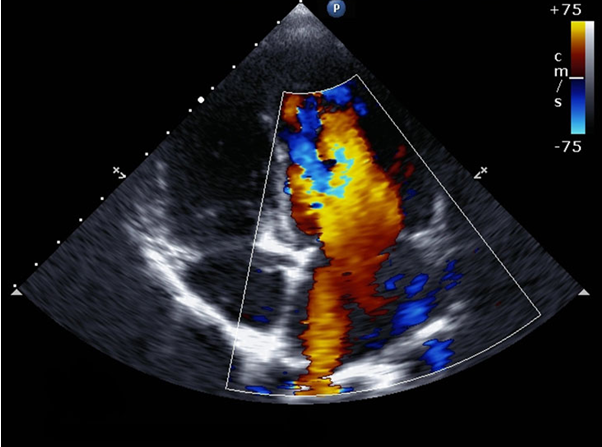
Doppler echocardiogram
Sound waves change pitch when they bounce off blood cells moving through your heart and blood vessels. These changes (Doppler signals) can help your doctor measure the speed and direction of the blood flow in your heart.
Doppler techniques are generally used in transthoracic and transoesophageal echocardiograms. Doppler techniques can also be used to check blood flow problems and blood pressure in the arteries of your heart — which traditional ultrasound might not detect.
The blood flow shown on the monitor is colorized to help your doctor pinpoint any problems.
Stress echocardiogram
Some heart problems, particularly those involving the arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle (coronary arteries)occur only during physical activity. Your doctor might recommend a stress echocardiogram to check for coronary artery problems. However, an echocardiogram can't provide information about any blockages in the heart's arteries.
In a stress echocardiogram:
- Ultrasound images of your heart are taken before and immediately after you walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike.
- If you're unable to exercise, you may get an injection of a medication to make your heart pump as hard as if you were exercising.
Types of Heart Scans
There are several different types of echocardiograms.
Transthoracic echocardiography
This is the most common type of echocardiography. It’s painless and non-invasive.
A device called a transducer will be placed on your chest over your heart. The transducer sends ultrasound waves through your chest toward your heart. A computer interprets the sound waves as they bounce back to the transducer. This produces the live images that are shown on a monitor.
Transoesophageal echocardiography
If a transthoracic echocardiogram doesn’t produce definitive images, your doctor may recommend a transoesophageal echocardiogram. In this procedure, the doctor guides a much smaller transducer down your throat through a thin, flexible tube in your mouth. They will numb your throat to make this procedure easier.
This tube is guided through your oesophagus, the tube that connects your throat to your stomach. With the transducer behind your heart, your doctor can get a better view of any problems.
Stress echocardiogram
A stress echocardiogram uses traditional transthoracic echocardiography. However, the procedure is done after you’ve exercised or taken medication to make your heart beat faster. This allows your doctor to test how your heart performs under stress.
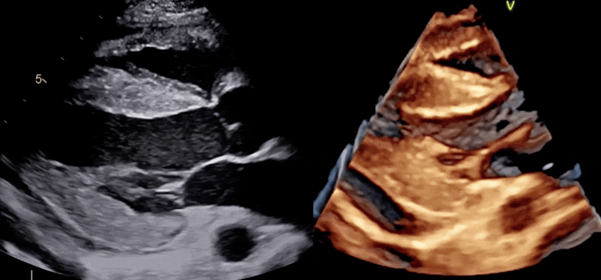
Three-dimensional echocardiography
A three-dimensional (3-D) echocardiogram uses either transoesophageal or transthoracic echocardiography to create a 3-D image of your heart. This involves multiple images from different angles. It’s used prior to heart valve surgery. It’s also used to diagnose heart problems in children.
Echocardiogram with bubble study
An echocardiogram shows the anatomy, structure and function of your heart.
A common type of echocardiogram is called a transthoracic echocardiogram. In this test, sound waves directed at your heart from a wandlike device (transducer) held on your chest produce video images of your heart in motion. Doctors may use this test to diagnose a patent foramen ovale and detect other heart problems.
Variations of this procedure may be used to identify patent foramen ovale, including:
Colour flow Doppler. When sound waves bounce off blood cells moving through your heart, they change pitch. These characteristic changes (Doppler signals) and computerized colourization of these signals can help your doctor examine the speed and direction of blood flow in your heart.
If you have a patent foramen ovale, a colour flow Doppler echocardiogram could detect the flow of blood between the right atrium and left atrium.
Saline contrast study (bubble study). With this approach, a sterile salt solution is shaken until tiny bubbles form and then is injected into a vein. The bubbles travel to the right side of your heart and appear on the echocardiogram.
If there's no hole between the left atrium and right atrium, the bubbles will simply be filtered out in the lungs. If you have a patent foramen ovale, some bubbles will appear on the left side of the heart. The presence of a patent foramen ovale may be difficult to confirm by a transthoracic echocardiogram.
Echocardiogram at home (mobile echocardiography)
We can also arrange echocardiograms at home if a patient is unable to travel to My Heart Clinic.
The mobile echocardiogram / heart scan requested by the physician can be done in your home environment by our experienced physiologists and subsequently analysed by our consultant cardiologists.
Risks
Echocardiograms are considered very safe. Unlike other imaging techniques, such as X-rays, echocardiograms don’t use radiation.
A transthoracic echocardiogram carries no risk. There’s a chance for slight discomfort when the electrodes are removed from your skin. This may feel similar to pulling off a band-aid.
There’s a rare chance the tube used in a transoesophageal echocardiogram may scrape the side of your oesophagus and cause irritation. The most common side effect is a sore throat. You may also feel a bit funny due to the sedative used in the procedure.
The medication or exercise used to get your heart rate up in a stress echocardiogram could temporarily cause an irregular heartbeat. The risk of a serious reaction is reduced because the procedure is supervised.
How to prepare for an echocardiogram
A transthoracic echocardiogram requires no special preparation.
However, if you undergo a transoesophageal echocardiogram, your doctor may instruct you not to eat anything for a few hours before the test. This is to prevent you from vomiting during the test. You may also not be able to drive for a few hours afterward due to the sedatives.
If your doctor has ordered a stress echocardiogram, wear clothes and shoes that are comfortable to exercise in.
After an echocardiogram
Your doctor will review your results after the test. The results may reveal abnormalities such as:
- Damage to the heart muscle.
- Heart defects.
- Heart size.
- Pumping strength.
- Valve problems.
If your doctor is concerned about your results, they may refer you to a cardiologist. This is a doctor who specializes in the heart. Your doctor may order more tests or physical exams before diagnosing you.
If you’re diagnosed with a heart condition, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that works best for you.

